Multi-axis CNC machining has revolutionized the manufacturing industry by enabling the creation of complex parts with unparalleled precision. This article breaks down the different types of multi-axis machining and their specific applications to help you choose the best technique for your manufacturing needs.
Three-Axis CNC Machining
Movement: Three-axis CNC machining operates along the X, Y, and Z axes. The workpiece remains stationary while the cutting tool moves along these three axes to shape the part.
Applications:
- Simple Parts: Ideal for creating straightforward geometries like plates, frames, and basic shapes.
- Flat Surfaces: Suitable for machining parts with flat surfaces and simple contours.
- Basic Milling: Frequently used for drilling, tapping, and milling operations in various industries such as automotive and consumer goods.
Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: Lower setup and operational costs make it suitable for less complex projects.
- Ease of Use: Simpler programming and shorter setup times compared to higher-axis machines.
Four-Axis CNC Machining
Movement: Four-axis CNC machining adds a rotational movement around the X-axis (often referred to as the A-axis) to the existing X, Y, and Z axes. This allows the workpiece to be rotated for additional machining flexibility.
Applications:
- Complex Parts: Used for more complex geometries that require machining on multiple sides, such as spiral cuts and engraved surfaces.
- Continuous Machining: Ideal for parts that need continuous machining around a fixed axis, like camshafts and turbine blades.
- Enhanced Detail: Suitable for intricate detailing and parts that require precise angular cuts.
Advantages:
- Increased Versatility: Allows for more complex parts without the need for multiple setups.
- Improved Accuracy: Reduces manual handling of the workpiece, maintaining higher accuracy.
Five-Axis CNC Machining
Movement: Five-axis CNC machining incorporates rotation around both the X and Y axes (A and B axes) in addition to the X, Y, and Z linear movements. This provides extensive flexibility, allowing the tool to approach the workpiece from almost any direction.
Applications:
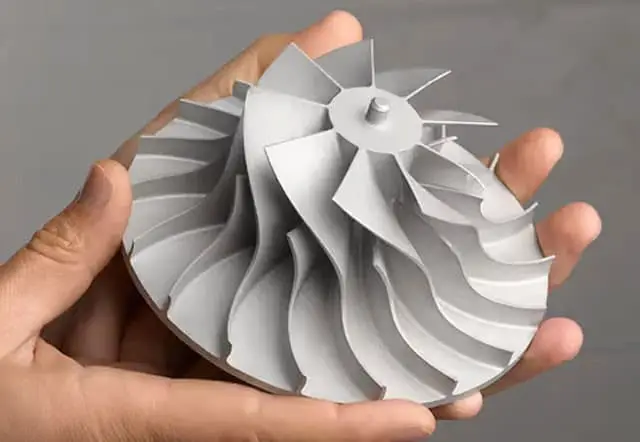
- Highly Complex Parts: Essential for manufacturing intricate parts that require detailed surfaces and complex geometries, such as aerospace components, medical implants, and intricate molds.
- Advanced Surface Machining: Ideal for parts with complex curves and angles, providing a superior surface finish.
- High Precision Components: Used in industries demanding the highest precision and accuracy, including aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing.
Advantages:
- Reduced Setup Time: Minimizes the need for multiple setups and repositioning, enhancing efficiency.
- Superior Quality: Provides unmatched precision and surface finish, crucial for high-performance applications.
- Greater Flexibility: Capable of machining intricate and detailed parts in a single setup.
Choosing the right multi-axis CNC machining technique depends on the complexity and precision required for your project. Three-axis machining is ideal for simpler parts and cost-effective solutions, while four-axis and five-axis machining offer enhanced capabilities for more complex and detailed components. By understanding these techniques, you can enhance your manufacturing capabilities, ensuring high-quality and efficient production for your specific needs.
Embrace the power of multi-axis CNC machining to take your manufacturing processes to the next level. Whether you’re producing simple frames or highly complex aerospace components, the right CNC machining technique can significantly improve your productivity and product quality.