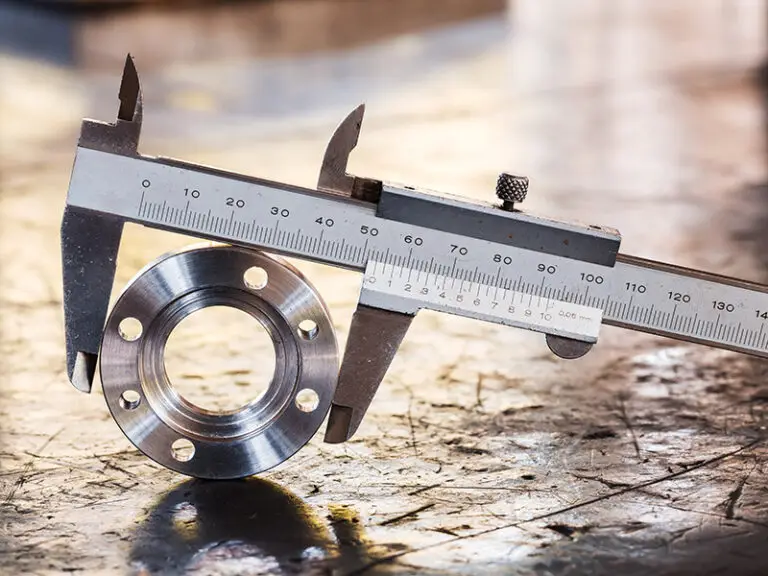
When it comes to manufacturing custom parts and products, both CNC machining and 3D printing are popular techniques. However, the choice between these methods often depends on the materials involved. Let’s delve deeper into the materials used in each process to help you determine which method best suits your needs.
Materials in 3D Printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, constructs objects layer by layer from various materials. Some common 3D printing materials include:
- Liquid Resin (SLA): Used in stereolithography, it’s ideal for creating highly detailed and complex parts.
- Nylon Powder (SLS): Selective laser sintering uses nylon powder for strong and durable prototypes.
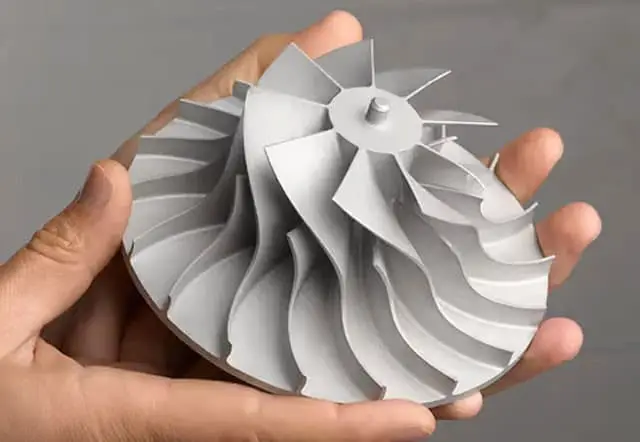
- Metal Powder (DMLS/SLM): Direct metal laser sintering or selective laser melting enables the creation of metal parts with complex geometries.
- PLA and ABS (FDM): Fused deposition modeling uses these common thermoplastics for a wide range of applications.
- Composite Filaments: Including carbon fiber or glass fiber-infused plastics for enhanced strength.
These materials allow for great flexibility in design and can produce intricate, complex shapes that might be challenging with traditional methods.
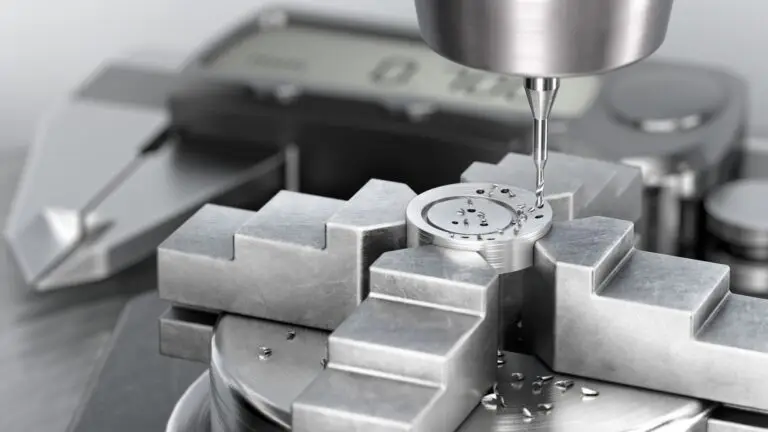
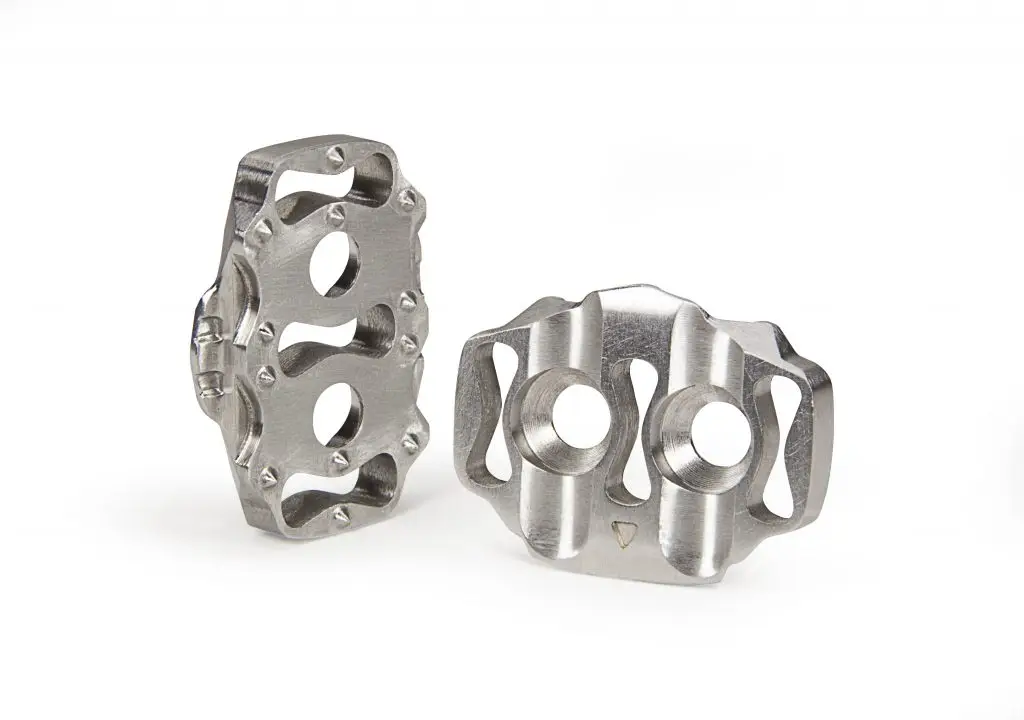
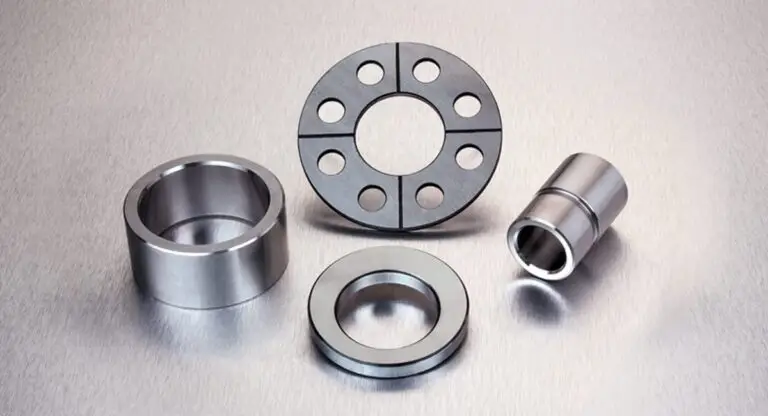
Materials in CNC Machining
CNC machining, or subtractive manufacturing, starts with a solid block of material and removes unwanted sections to create the final product. The materials used in CNC machining include:
- Metals: Aluminum, steel, brass, titanium, and exotic alloys.
- Plastics: ABS, polycarbonate, nylon, and high-performance engineering plastics.
- Composites: Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers and other composite materials.
The range of materials available for CNC machining is vast, offering more options compared to 3D printing. This is especially beneficial when working with high-performance plastics and exotic alloys that might not be feasible for 3D printing.
Making the Right Choice
Choosing the right material is critical for the success of your project. If you need a prototype with high strength, durability, and resistance to wear and tear, CNC machining with metals or high-performance plastics might be the best option. On the other hand, if you are developing a complex, detailed prototype that requires intricate design features, 3D printing with liquid resin or metal powder could be more suitable.
By understanding the material capabilities of CNC machining and 3D printing, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your project’s requirements.