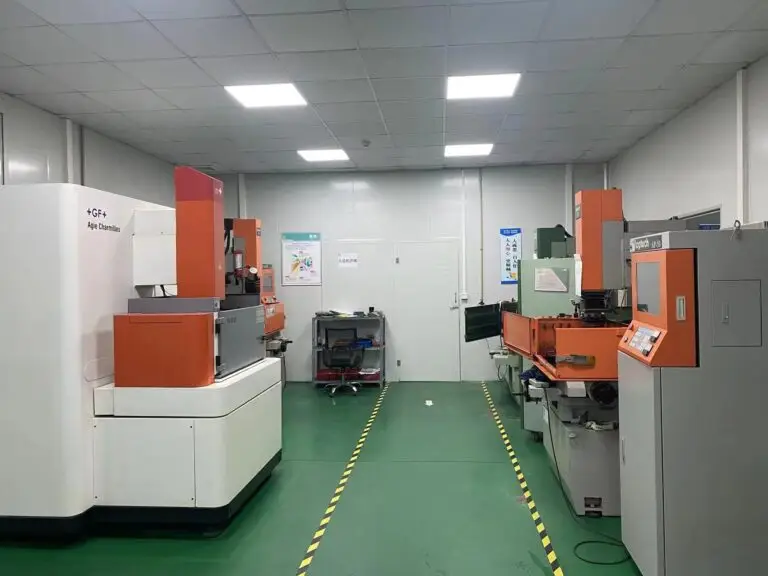
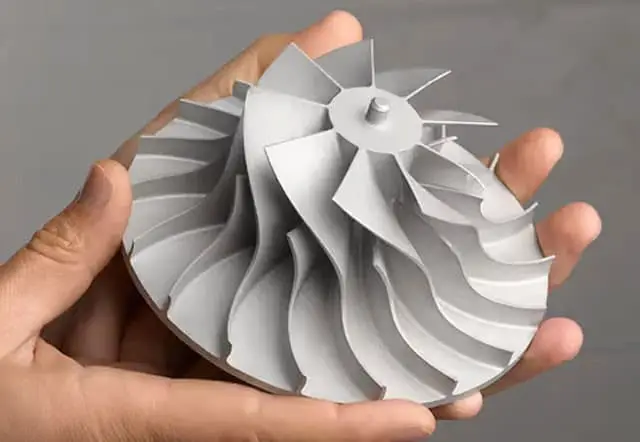
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining encompasses various techniques, each tailored to specific manufacturing needs. Understanding these techniques is crucial for selecting the right process for your project, ensuring high-quality and efficient production. This guide explores the main CNC machining techniques and their applications.
CNC Milling
Process: CNC milling uses rotating cutters to remove material from a workpiece. The machine can move the workpiece along multiple axes to create complex shapes and surfaces.
Applications:
- Complex Shapes: Ideal for creating intricate and detailed parts with various geometries.
- Surface Finishing: Provides excellent surface finishes for aesthetic and functional components.
- Versatile Material Use: Suitable for metals, plastics, and composites, making it perfect for industries like aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics.
Benefits:
- High Precision: Achieves tight tolerances and detailed features.
- Repeatability: Ensures consistent quality in large production runs.
- Flexibility: Capable of producing a wide range of parts, from simple to complex designs.
CNC Turning
Process: CNC turning rotates the workpiece while a cutting tool shapes it. This method is highly efficient for producing cylindrical parts by removing material from the outside diameter of the rotating workpiece.
Applications:
- Cylindrical Parts: Perfect for manufacturing shafts, bolts, and nuts.
- Symmetrical Objects: Suitable for creating parts with radial symmetry.
- High-Speed Production: Ideal for high-volume production runs in industries like automotive and heavy machinery.
Benefits:
- Speed and Efficiency: Rapid production with minimal downtime.
- Precision: Produces parts with smooth finishes and exact dimensions.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces material waste and machining time for cylindrical components.
CNC Drilling
Process: CNC drilling creates precise holes in a workpiece using rotating drill bits. The drill bit is advanced into the material to form holes of various sizes and depths.
Applications:
- Assembly Parts: Commonly used for creating holes for screws, bolts, and other fasteners in assembly processes.
- Mass Production: Efficient for high-volume production in industries like electronics and automotive.
- Varied Materials: Effective for drilling through metals, plastics, and composites.
Benefits:
- Accuracy: Ensures precise hole placement and consistent diameters.
- Speed: Quick drilling operations for high-efficiency production.
- Versatility: Suitable for various materials and hole sizes.
CNC Threading
Process: CNC threading cuts threads on the internal or external surface of a workpiece. This technique is crucial for creating screw threads that are used in various fastening applications.
Applications:
- Fasteners: Essential for manufacturing screws, nuts, and bolts.
- Pipe Fittings: Used in plumbing and construction for creating threaded pipe connections.
- Precision Components: Ideal for producing high-precision threaded parts in industries like aerospace and medical devices.
Benefits:
- Consistency: Produces uniform and precise threads with each pass.
- Durability: Creates strong and reliable threaded connections.
- Efficiency: Speeds up the production of threaded parts compared to manual threading.
Understanding different CNC machining techniques helps you choose the best process for your manufacturing needs. Whether you need intricate shapes, precise holes, or reliable threaded parts, CNC machining offers versatile and efficient solutions. By selecting the right technique, you can ensure high-quality production and meet the specific demands of your industry.